5.1/ Good practice
- Todo:
- Create a pacckage like ci_integration that depends on Dynamic Graph and show the implementation of the dg_ci_example.
If possible, controllers and helper functions should be implemented in "dg_tools". Please refer to the project's readme about the desired code structure.
- Todo:
- cleanly split between a simulated example (currently shown with stuggihop) and a hardware example (currently at the bottom with a single motor...).
5.2/ Writing a simple entity
In dynamic graph, an entity is an object that consumes input signals and provides output signals. For instance, a P-controller might consume the current position of a motor as input signal and provide as output a torque command to move the motor position towards a desired position.
To control a robot / simulator using dynamic graph manager, the following is necessary:
- Implement a controller as a dynamic graph entity.
- Example:
- Expose the entity using a few lines in CMakeList.txt
- Example:
- In the python interpreter of the dynamic graph manager, create the control graph, connect it to the robot device and run configurations if needed
- Example (TODO: make an example contained in dg_tools):
5.3/ Expose the entities to Python
Once you have defined the controller in C++, you need to expose it to python. This is done by adding a few lines into the CMakeList.txt file.
For an example, please refer to https://git-amd.tuebingen.mpg.de/amd-clmc/dg_tools/blob/master/src/CMakeLists.txt.
- First add your entities here:
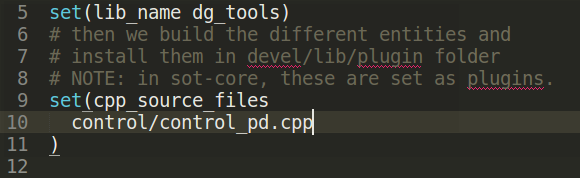
- Secondly export the python bindings:
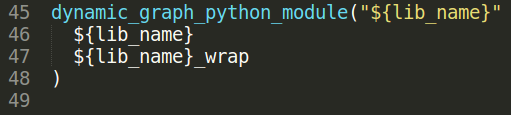
5.4/ Create the control graph entries and connect them to the robot
An example on how a simple control graph using the MotorController with the robot.device is shown in single_motor_main.py. Note that robot.device is provided by the Dynamic Graph Manager automatically and initialized to talk to the real/simulated hardware. The robot.device is created from the yaml file's device specification. Especially, all the input and output signals are created on the robot.device as described in the sensor and control part of the yaml file.
